Forskelle på
SLS, SLA og FDM-print
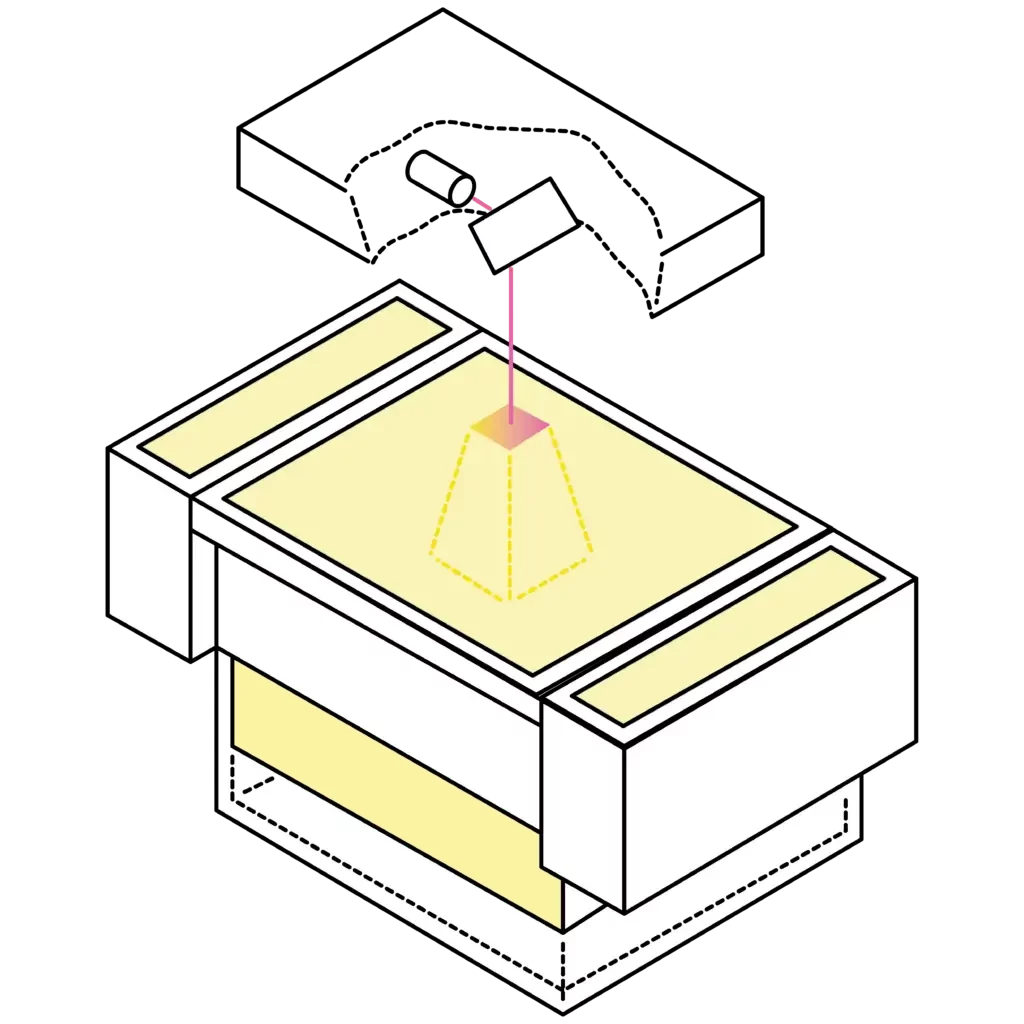
SLS-print
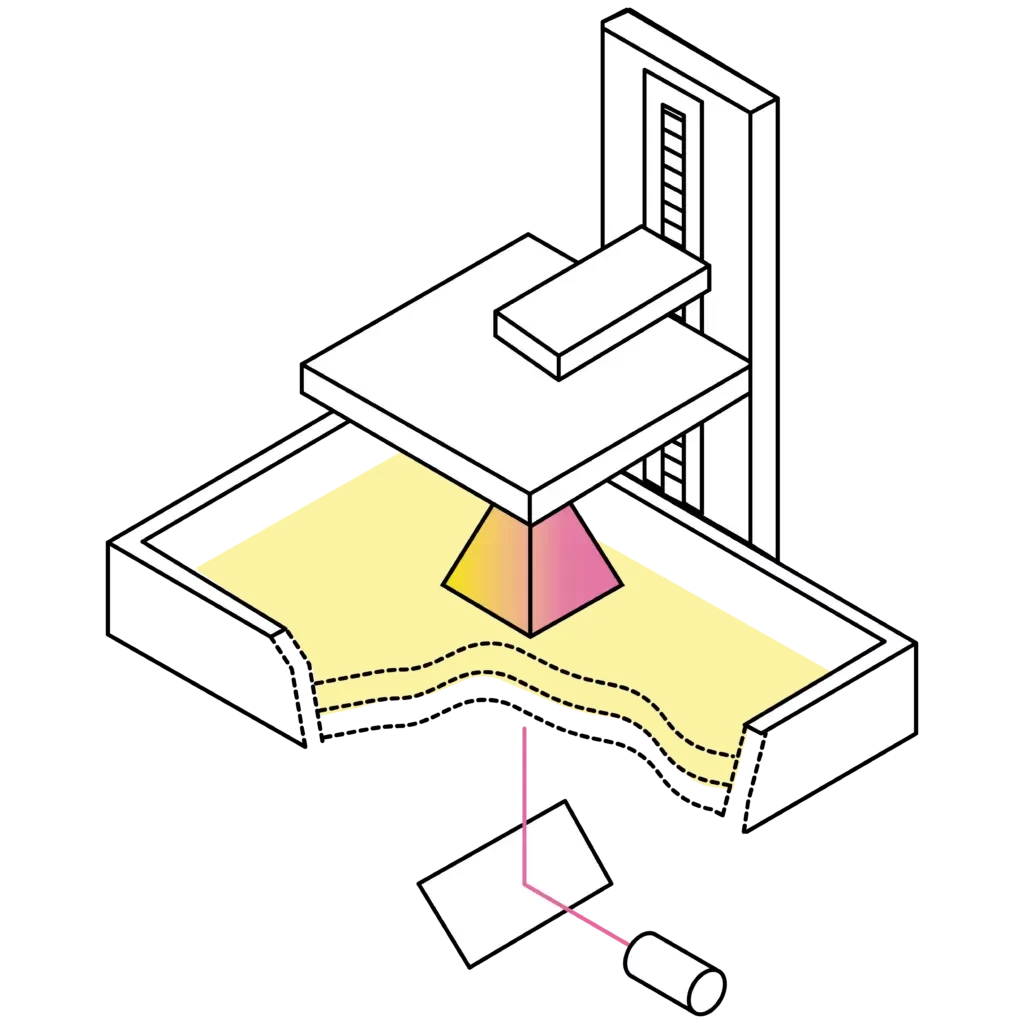
SLA-print
FDM-print
Differences in 3D printing technologies
SLS | SLA | FDM | |
|---|---|---|---|
Advantages | SLS printing has strong functional parts
With SLS printing, there is great design freedom There is no need for support structures in SLS printing SLS printing achieves a good finish and therefore has a visually attractive appearance” | SLA printing has high accuracy
SLA printing has a smooth surface finish SLA printing has a range of functional applications | FDM printing involves low-cost consumer machines and materials
FDM printing is quick and easy for simple, small parts |
Disadvantages | SLS printing has a rough surface finish.
SLS printing is limited in material selection. | SLA printing is sensitive to prolonged exposure to UV light. | FDM printing has low accuracy.
FDM printing is limited to low-level details. FDM printing has limited design compatibility. |
Applications | SLS printing is used for functional prototyping.
Low volume manufacturing, bridge manufacturing, or custom manufacturing. | SLA printing is used for functional prototyping.
Patterns, molds, and tooling. Dental applications. Prototyping. Model making. |
FDM printing is used for low-cost rapid prototyping.
FDM printing is used for basic proof-of-concept models. |
Material | SLS printing is made with engineering thermoplastics such as Nylon 11, Nylon 12, and Nylon GF30. | SLA printing is done using variants of resin (thermosetting plastic).
Standard, engineering (ABS-like, PP-like, flexible, heat-resistant), castable, dental, and medical (biocompatible). | FDM printing is done using standard thermoplastics such as ABS, PLA, and their various blends. |
Price level | Medium | Expensive | Cheap |